Solar Thermal Application:
The sun’s energy can be collected directly to create both high temperature steam (greater than 100oC) and low temperature heat (less than 100oC) for use in a variety of heat and power applications.
Low temperature solar thermal systems collect solar radiation to heat air and water for industrial applications including: Process industry, boiler feed, laundry and canteens.
- Agricultural sector, hatcheries and dairies.
- Process industry, Boiler feed, Laundry and canteens.
- Agricultural sector, hatcheries, and dairies.
- Swimming pool heating.
- In-process heating.
- Health clubs (Steam / Sauna).
- Forced circulation based systems.
- Hotels, resorts, hospitals and hostels.
Solar Water Heating System:
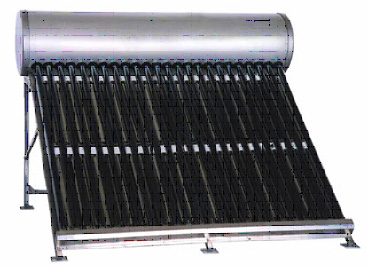
A solar water heater consists of a collector to collect solar energy and an insulated storage tank to store hot water. The solar energy incident on the absorber panel coated with selected coating transfers the heat to the riser pipes fitted underneath the absorber panel. The water passing through the risers get heated up and is delivered to the storage tank. The re-circulation of the same water through abosrber panel in the collector raises the temperature to 80oC (Maximum) in a good sunny day. The total system with solar collector, storage tank and pipelines is called solar hot water system. Broadly, the solar water heating systems are of two categories. They are closed loop system and open loop system. In the first one, heat exchangers are installed to protect the system from hard water obtained from bore wells or from freezing temperatures in the cold region. In the other type, either thermosyphon or forced circulation system, the water in the system is open to the atmosphere at one point or other. The thermosyphon systems are simple and relatively inexpensive. They are suitable for domestic and small institutional systems, provided the water is treated and potable in quality. The forced circulation systems employ electrical pumps to circulate the water through collectors and storage tanks. The choice of system depends on heat requirement, weather conditions, heat transfer fluid quality, space availability, annual; solar radiation, etc. The SHW systems are economical, pollution free and easy for operation in warm countries like outs.
Based on the collector system, solar water heaters can be of two types.
1. Flat Plate Collectors (FPC) based Solar Water Heaters (SWH)

The Solar radiation is absorbed by Flat Plate Collectors which consists of an insulated outer metallic box covered on the top with glass sheet. Inside there are blackened metallic absorber (selectively coated) sheets with built in channels or riser tubes to carry water. The absorber absorbs the solar radiation and transfers the heat to the flowing water. There are 83 BIS approved manufacturers of Solar Flat Plate Collectors.
Evacuated Tube Collector is made of double layer borosilicate glass tubes evacuated for providing insulation. The outer wall of the inner tube is coatedwith selective absorbing material. This helps absorption of solar radiation and transfers the heat to the water which flows through the inner tube. There are 14 MNES approved ETC based solar water heating suppliers. However, this being a new technology, it is advised that before installing the ETC based system, the buyer should ensure proper specification and test reports of the system issued by the Ministry of Non-conventional Energy Sources, Govt. of India. Solar water heating is now a mature technology. Wide spread utilization of solar water heater scan reduce a significant portion of the conventional energy being used for heating water in homes, factories and other commercial and institutional establishments. Internationally the market for solar water heaters has expanded significantly during the last decade.
Estimates Of Requirement Of Hot Water –Some Useful Thumb Rules
| Application | Typical Requirementof Hot Water at 60 C |
| Household bathing using buckets | 10-20 liitres per person per bath |
| Household bathing using shower | 20-30 Litres for 10 Minute bath |
| Shaving, while a tap runs | 10-15 Litres |
| Household bathing in bathtub ( one filling) | 75-100 Litres |
| Wash basin ( hand wash, brushing of teeth, etc.) | 3-5 Litres per person per day |
| Kitchen washing | 2-3 Litres per person per day |
| Dish washer | 40-50 Litres per washer cycle |
| Clothes washing machine | 7-110 Litres per Wash cycle |
| Industrial Canteen | 3-5 Litres per worker per day |
| Small unstarred hotels | 30-40 litres per occupant per day |
| Starred hotels | 100-150 Litres per room per day |
| Hospitals | 10-15 Litres per bed per day |
Multistoreyed apartments
|
|
Mandatory Use Of Solar Water Heating Systems: Vide Delhi Government Gazette Notification No. F.11 (149)/2004-Power/2387 dated 28/09/2006, the use of solar water heating systems will be mandatory in the following categories of buildings, namely:-
- Industries where hot water is required for processing;
- Hospitals and Nursing homes including Government Hospitals;
- Hotels, Motels or Banquet halls;
- Jail Barracks.
- Large Canteens having the capacity to serve more than one hundred persons in a day.
- Corporate buildings located on plots having an area of Five Hundred square meters and above.
- All residential buildings built on a plot having an area of Five Hundred square meters or above falling within the National Capital Territory of Delhi, excluding Delhi Cantonment Area or areas exempted under section 61 of the Energy Conservation Act, 2001.
- All Government buildings, residential schools, educational colleges, hotels, technical or vocational education institutes, district institutes of education And training, tourism complexes and universities etc.
Scheme/Subsidy for Solar Water Heater: The EE & REM CENTRE, Department of Environment, Govt. Of NCT of Delhi provides subsidy / Rebate / Incentive to offset initial cost of the system, reduce payback period.
Non Commercial Sector: Consequent upon the Cabinet decision no.1309 dated 20.11.07 for promotion of Solar Water Heating System (SWHS) by Non-Commercial Institutions (NCI) like Colleges, Hostels, Old Age Homes, Orphange, Religious Establisment, Charitable Institutions, Group Housing Societies etc. through a scheme of incentive/rebate to extent of Rs.6000 per every 100 lpd (litres per day) SWHS and up to a maximum amount of Rs. 60,000 for 1000 lpd system installed.
Domestic Sector: A subsidy scheme is also available in Domestic sector for Promotion of Solar Water Heating System in Domestic Sector. Through this scheme, an fixed incentive/rebate of Rs.6000 is given on installation of Solar Wter heating Systems.
High temperature solar thermal systems: use mirrors and other reflective surfaces to concentrate solar radiation. Parabolic dish systems concentrate solar radiation to a single point to produce temperatures in excess of 1000oC Line-focus parabolic concentrators focus solar radiation along a single axis to generate temperatures of about 350oC. Central receiver systems use mirrors to focus solar radiation on a central boiler. The resulting high temperatures can be used to create steam to either drive electric turbine generators, or to power chemical processes such as the production of hydrogen.
Solar Concentrating System for heating air / generating steam directly or through heating of oil:
Under this programme, Solar Concentrating systems comprising of parabolic dishes known as “Scheffler” dishes have been found to be useful for generating steam to cook food for 100 and 10000 of people in Community Kitchens specially at religious places. MNES, Govt. of India shall provide 50% of the cost of the system subject to a maximum of Rs.5,000/- per sq. mtr. of dish area for Solar Concentrating Systems for non-profit making institutions/ organizations. 35% of the cost of system subject to maximum of Rs.3500/- per sq. mtr. of dish area for Solar Concentrating Systems for commercial / industrial organizations (profit making and claiming depreciation). List of known manufacturers/suppliers involved in installation of solar concentrating systems for steam applications/direct cooking.

 ऊर्जा दक्षता एवं नवीकरणीय ऊर्जा प्रबंधन केंद्र
ऊर्जा दक्षता एवं नवीकरणीय ऊर्जा प्रबंधन केंद्र 


